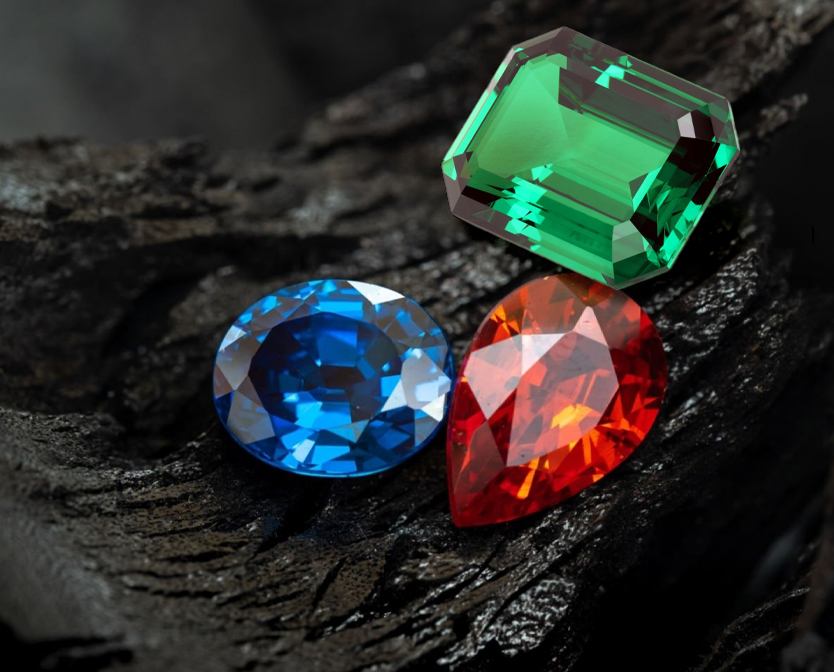
Explore fascinating details about your preferred gemstones, and gain insights into gemstone cuts, clarity, color and beyond.
Gemstones come in an endless array of types. Some gemstones, such as sapphire, come in various colors like blue sapphire, yellow, and green gem. Let's delve into the details of a few renowned gemstones.
Factors of Quality
Similar to diamonds, a multitude of factors influence the quality of a gemstone. Let's examine each of these factors thoroughly to comprehend how they assist us in assessing the quality of a gemstone.
Color
All gems consider color to be very important and evaluate it in a similar way for each type. These three color elements determine the gemstone quality in the jewelry sector.
- Hue
Hue refers to the fundamental or distinct color of the gemstone. In other words, hue characterizes the shade, tint, or perception of a color.
- Tone
Tone denotes the intensity of a gemstone's hue, varying from clear to pitch black. In simpler terms, we describe tone as the relative lightness or darkness of a Hue. We describe gemstone tone as 'light', 'medium-light', 'medium', 'medium-dark', and 'dark'. The majority of individuals regard the tone ranging from medium-light to medium-dark as the most precious.
- Saturation
Saturation refers to the degree of intensity or clarity of a gemstone's hue or color. A gemstone without gray or brown colors is very saturated and worth more than a less saturated gemstone. Saturation often determines the cut of a gemstone. A cut of superior quality ensures a consistent color across the stone and reveals the least number of inclusions.
Precious gemstones can be any color, and one gemstone can have many different shades and hues. Garnet comes in many rich colors, while Sapphires can be pink, yellow, deep blue or green color.
Attention: Gemstone treatments enhance their look or longevity and require specific maintenance.
Definition of Clarity
Clarity pertains to the presence or absence of flaws inside or on the surface of a gemstone. Perfect gemstones are uncommon and costly. Examining closely or using a 10x magnification can reveal minor defects in most valuable gems. A gem may have imperfections such as inclusions, cracks, spots, clouds, or any other type of defect or blemish.
A scale grades diamonds from flawless to included 3, while colored stones have their own grading scale. Three 'Types' define the classification of precious stones based on different habits of clarity.
- Category I
Category I colored gems are those with few or no flaws. Examples include Aquamarine, Blue Topaz, Zircon, Morganite, and Tanzanite. We grade Type I stones from VVS (hardly seen to seen), VS (a little), SI1 (obvious), SI2 (clear) to I (included).
- Category II
Type II gemstones have very few flaws. Examples of Type II gemstones include Corundum, Garnets, Iolite, Peridot, Quartz (including Amethyst, Citrine, Ametrine), Ruby, Sapphire, Spinel, and more. We evaluate the clarity of this Type II category. The clarity grading ranges from VVS (minor), VS (noticeable), SI1 (obvious), SI2 (prominent), to I (prominent, impacting visual appeal).
- Category III
Category III colored gems typically always contain inclusions. Gems in this category can encompass Emeralds, Tourmaline, and so on.
In Type III classification, clarity is categorized into different levels. These levels are VVS (noticeable), VS (Obvious), SI1 (prominent), SI2 (more prominent), and I1 (affecting appearance or durability). Each level represents a certain degree of detectability, transparency, or observability. The VVS level is the least observable, while the I1 level has the most noticeable effect on appearance or durability.
- Inclusions and Value
Gemstones, being products of nature, often contain inherent impurities known as 'inclusions'. These inclusions are unique to each stone, thus they are also termed as 'birthmarks'. Some inclusions contribute to the gemstone's distinctiveness and lend an unusual design element to it.
Engagement rings can feature a variety of gemstones in addition to, or instead of, the traditional diamond. Emerald and Red Tourmaline have inclusions, while Citrine, Green Tourmaline, and Aquamarine are usually flawless. Extremely minute inclusions are not visible to the unaided eye, rendering the gemstone rare and correspondingly costly.
Carat Weight and Rarity
Gemstones have their value based on their weight, not their dimensions. We measure the weight of these gems in carats, where one carat equals one-fifth of a gram.
Gemstones of the same size can have different weights because they have different densities, which is their mass per unit volume. For example, a one-carat Emerald and a one-carat Ruby may have the same weight. However, their sizes will be different.
This occurs because they consist of different minerals. These minerals have varying densities.
People seldom see larger sizes of gemstones such as Rubies, Emeralds, Sapphires, and Tsavorite Garnet. These valuable gems, when found in larger sizes, demand a considerably higher price per carat than their smaller counterparts. Larger sizes commonly contain gemstones such as Amethyst, Citrine, Blue Topaz, and Amber. As a result, their price per carat remains constant regardless of their size.
Cut and Beauty
Nature creates gemstones, but a skilled gem cutter brings out their brilliance and beauty. Nature forms gemstones naturally. However, it requires a skilled gem cutter to enhance their brilliance and beauty.
The amount of white light that reflects to the eye clean determines brilliance. Conversely, attractiveness is a product of the amalgamation of hue, cut precision, and surface aesthetics.
When we talk about cut, we are referring to two distinct aspects.
The three-dimensional design encompasses shapes like the marquise, round cut, oval cut, and so on.
The brightness and attractiveness come from the high-quality cutting, which depends on the accuracy of the angles and proportions. It's how a gemstone reflect light and draws the eye. A good cut should be symmetrical and have colorful light reflections. If a cut is asymmetrical, it means it is of low quality.