Purchasing a diamond for an engagement ring or other jewelry is special. It is one of the most beautiful gifts a person or family can give to someone they care about. It holds a special place in their hearts.
A diamond is more than a stone. It holds the best memories, many feelings and emotions. Most importantly, it reminds the wearer that they have the giver's heart forever.
A diamond is valuable because of the passion, sentiment and enthusiasm it symbolizes. For you to keep it, it must be flawless. Then you must understand the characteristics of a diamond that make it exceptional and flawless.
Lab grown diamonds are less expensive and as durable as natural diamonds. The use of lab-grown diamonds in diamond engagement ring and other diamond jewelry is growing in popularity. But before making a purchase, you should always be aware of what you're purchasing. Read this article to discover the truth about lab-grown diamonds.Diamonds are primarily graded based on four characteristics: Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat i.e. 4 cs of natural diamond. Every consumer should be aware of how these four factors influence both physical appearance and chemical characteristics. Let us go through this one by one.
The 4C’s Of Diamond
Cut

The letter C denotes the cut of a diamond. For quality diamonds, having the right cut grade is essential for enhancing the stone's overall brilliance.
The diamonds cut influences the overall appearance of a natural or lab grown diamond. It also indicates the gem's proportion, symmetry, and polish
To effectively interact with light, a rough diamond must undergo faceting. Each side of the stone is cut differently. This enables the stone to interact with light properly.
Upon reaching a diamond, light rays ought to fracture and reflect in various directions, resulting in a recognizable shimmer. To accomplish this, a diamond craftsman must cut a rough diamond in such a way that it has proportion and symmetry.
Effort, attention to detail, and past experience are essential for achieving a great cut. Taking the time to ensure the correct amount of effort is invested is key.
An eye for detail helps to ensure accuracy. Drawing on past expertise will ensure the best possible result. The ultimate result is a visually pleasing stone that is suitable for mounting on a ring of choice.
Color
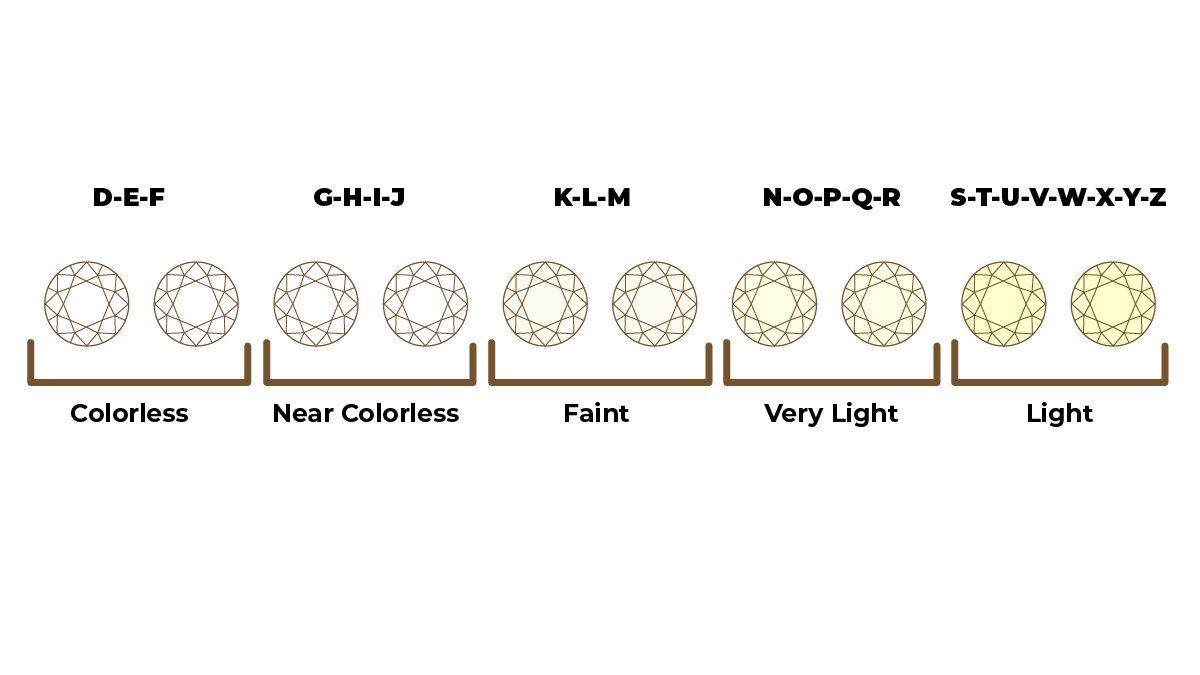
The second C is for color. And you need to understand that before selecting your lab grown diamond or natural diamond. You might suppose it relates to fancy colored diamonds like red, orange, and green.
However, this is not the case. The color of a diamond is the absence of color in the gemstone! Jewelers color grading lab diamonds using the International Gemological Institute's (IGI) D to Z grading scale.
Each letter from D to Z indicates the amount of pigment (not the hue) and is graded accordingly. D is colorless diamonds, while Z is bright in color. D is the rarest and represents the most valuable stones on the scale. As you get closer to Z, each letter has a little more color than the last, which reduces its value.
Clarity
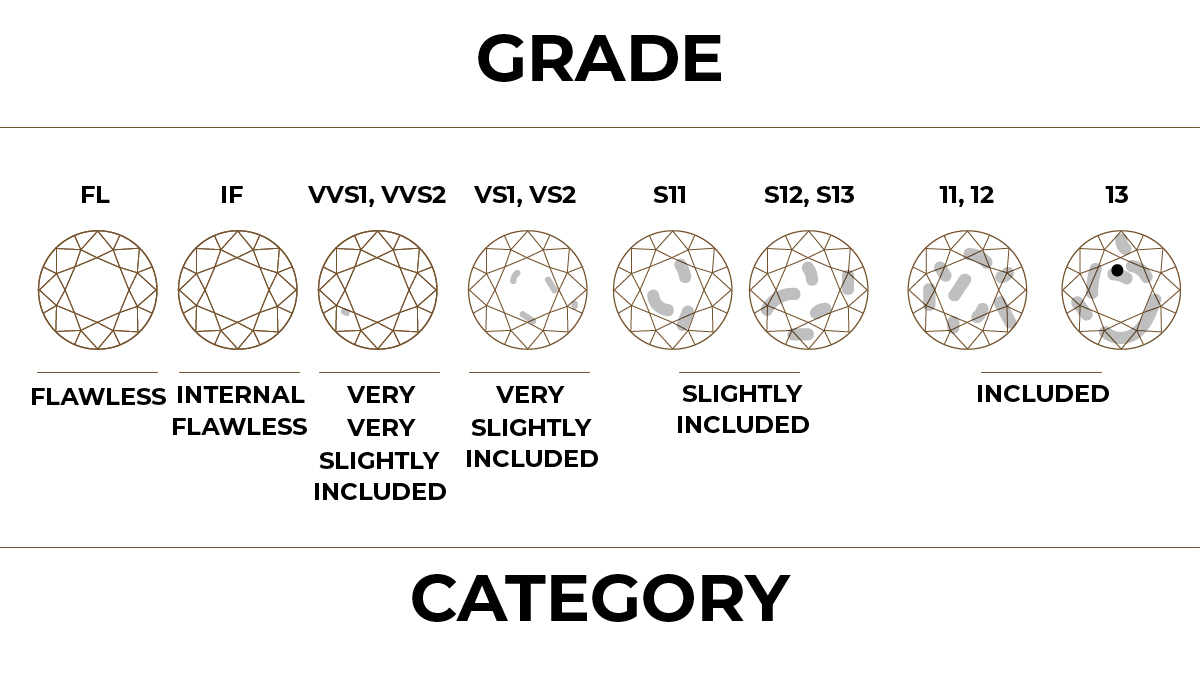
The Third C stands for clarity. Both lab created diamonds and natural stones may contain flaws and imperfections. Blemishes are imperfections on the surface of the stone. And inclusions are marks within the stone.
Diamond graders must examine these flaws and blemishes to determine the clarity of the gem. The assessment of these elements is dependent on the quantity, size, and position of each of the variables listed. A 10x magnifying glass is used by the graders to analyze and rate the degree of clarity of the diamond.
The diamond clarity scale has been further divided into six segments.
a) Flawless (FL)
FL diamonds are precious stones that lack any blemishes or defects. These diamonds are the rarest and have the highest clarity rating.
b) Internally Flawless (IF)
IF the stones have no clear inclusions. FL diamonds are ranked in terms of clarity. IF stones are second on the scale.
c) Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2)
VVS1 and VVS2 diamonds have minor inclusions that are difficult to see. The minute imperfections in these diamonds are so small that they are difficult to see even with a 10x magnifying glass.
d) Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2)
Minor inclusions are visible only with extra effort from the grader in VS1 and VS2. Even if they are not flawless, they are regarded high-quality stones.
e) Slightly Included (SL1 and SL2)
Minor visible inclusions can be found in SL1 and SL2 diamonds. Inclusions may be too small to be seen without a magnifying lens. Therefore, it is necessary to use a magnifying lens to detect them.
f) Included (I1, I2, and I3)
I1, I2, and I3 have clear inclusions that can impact a diamond's clarity and brightness.
Carat

The fourth C stands for diamond carat weight. Carat focuses on the weight and size of lab grown diamonds. The carat weight of a mined diamond usually affects the price.
Lab-grown diamonds cost around 40% less than mined diamonds. You can buy a huge lab-grown diamond with the same size, brightness, and sparkle as a genuine diamond.
Before buying a lab-grown diamond, consult an expert. The diamond grading report and certification should follow the 4'Cs of diamonds.
Lab-grown diamonds have become a significant component of the diamond industry. It has grown in popularity and is clearly here to stay.
Are the Lab Grown Diamond Same as Natural Diamond?

Natural diamonds and lab grown diamonds appear identical, having the same hardness level and durability. Lab Diamonds were officially recognized as authentic by the Federal Trade Commission in the year 2018. But can lab-created diamonds be identified as genuine?
Yes. Since 2007, the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) has been grading diamonds that are created in a laboratory. Starting on July 1, 2019, the GIA Laboratory-Grown Diamond Reports and identification reports will no longer use the word "synthetic." The reports will still feature the typical GIA standards for grading color, clarity, and cut.
A Lab Grown Diamond and a Natural Diamond with equal 4 C's features look indistinguishable to the naked eye. Because lab grown diamonds have the same physical and chemical qualities as natural diamonds, they will be just as dazzling.
Gemologists can distinguish between lab grown diamonds and natural diamonds based on the presence or absence of trace levels of nitrogen. While natural diamonds take millions of years to form, lab grown diamonds do not contain any nitrogen.
This is done by the pressure of the earth's crust. After being formed, they are mined. Then, they are cut and polished.
In a laboratory environment, a Lab Grown Diamond undergoes the same examinations as a naturally formed diamond. The procedure utilized to generate a Lab Grown Diamond reduces the growing time from millions of years to a few months. The Lab Diamond is then cut and polished as natural diamond.
Conclusion

Independent gemological organizations rate quality lab-grown diamonds using the 4Cs: cut, color, clarity, and carat weight. Lab-grown diamonds, like natural diamonds, will display differences across the 4Cs and range in grade from poor to excellent. Although lab diamonds are actual diamonds, we believe you are referring to earth-mined diamonds.
The primary distinction between lab diamonds and earth-mined diamonds is their creation. Natural diamonds originate eons ago in the Earth's mantle at a very slow rate. Lab-made diamonds are made in two different ways. These are in a High-Pressure High Temperature chamber or a Chemical Vapor Deposition chamber.
Prior to buying a diamond, understanding how to select the ideal diamond will influence how you select your engagement ring. Before selecting an engagement ring, it is important to have a good understanding of diamonds. This includes understanding their structure and the 4C's.

